How Does Microsporidia Lie to Travel? Reveal Hidden Secrets!
Where is Microsporidia Found?
Microsporidia are ubiquitous, found in a wide range of environments, including soil, water, and even air. They infect vertebrates and invertebrates, thriving in diverse habitats:
- Natural Reservoirs: Storks, fish, insects, and mammals are common hosts.
- Human Habitats: Found in contaminated water and food.
- Geographic Distribution: Global, with higher prevalence in tropical and subtropical areas.
How Does Microsporidia Lie to Travel?
Microsporidia are fascinating, microscopic fungi that have puzzled scientists for decades. These obligate intracellular parasites have developed intricate strategies to infect hosts, spreading efficiently across species and geographic locations. They are known to affect various organisms, including humans, with severe implications for health and ecosystems.
Understanding how microsporidia travel and adapt is vital for combating the infections they cause. Their methods of transmission, survival, and persistence showcase their cunning ability to outwit immune defenses and environmental challenges.
How Does Microsporidia Spread?
The mode of transmission for microsporidia involves the ingestion or inhalation of infectious spores. These spores, resistant to environmental extremes, can persist for long periods.
- Direct Contact: Through fecal-oral contamination.
- Waterborne Transmission: Contaminated water is a significant source.
- Foodborne Spread: Ingestion of contaminated food can lead to infections.
- Zoonotic Transmission: Animals like birds and insects can act as reservoirs.
The Portal of Entry for Microsporidia
Microsporidia invade the host through specific entry points, such as:
- Respiratory Tract: Inhalation of spores from the environment.
- Gastrointestinal Tract: Consuming contaminated food or water.
- Ocular Infection: Spores entering through the conjunctiva.
How Does Microsporidia Lie to Travel?
Microsporidia have developed deceptive tactics to move between hosts. Their spores are encased in a tough, resistant wall, ensuring survival in harsh conditions. They utilize environmental mediums like water and soil, or hitch rides on intermediate hosts, such as insects.
- Mosquitoes and Microsporidia: Certain species, like Anopheles arabiensis, can act as vectors.
- Bird Hosts: Storks and other birds often carry spores over long distances.
These strategies highlight the parasite’s adaptability and resilience, ensuring their presence across the globe.
Who are the Common Victims of Microsporidia?
While microsporidia infect a wide range of hosts, certain populations are more vulnerable:
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Patients with HIV/AIDS or undergoing organ transplants.
- Children and the Elderly: Weakened immune systems make them susceptible.
- Animals: Fish, insects, and birds are frequent hosts.
Interestingly, birds cannot be affected by microsporidia in the same way humans are, but they still act as reservoirs for transmission.
Symptoms Caused by Microsporidia
The symptoms of microsporidiosis vary depending on the site of infection:
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea.
- Respiratory Issues: Chronic cough and difficulty breathing.
- Ocular Symptoms: Redness, pain, and vision problems.
- Neurological Signs: Headaches and confusion in severe cases.
E. cuniculi During the Multiplication Phase
One notable species, Encephalitozoon cuniculi, demonstrates remarkable efficiency during its multiplication phase in the cytoplasm of host cells. This phase is critical for its survival and dissemination.
How Deadly is Microsporidia?
The danger posed by microsporidia depends on various factors:
- To Humans: On a scale of 1-10, its severity ranges between 6-8 for immunocompromised patients.
- Numerical Statistics: Microsporidia infections have a mortality rate of approximately 10% in vulnerable populations.
- Impact on Animals: Devastating effects in fish farming and wildlife.
Can Microsporidia be Killed?
Effective treatments and preventive measures are available, including:
- Antifungal Medications: Drugs like albendazole and fumagillin.
- Boiling Water: Ensures spores in water are neutralized.
- Hygiene Practices: Reducing exposure to contaminated sources.
Prevention of Microsporidiosis
Preventing microsporidiosis involves:
- Safe Water Practices: Boil or filter drinking water.
- Proper Sanitation: Maintain cleanliness to avoid contamination.
- Protective Measures: Wear gloves when handling animals.
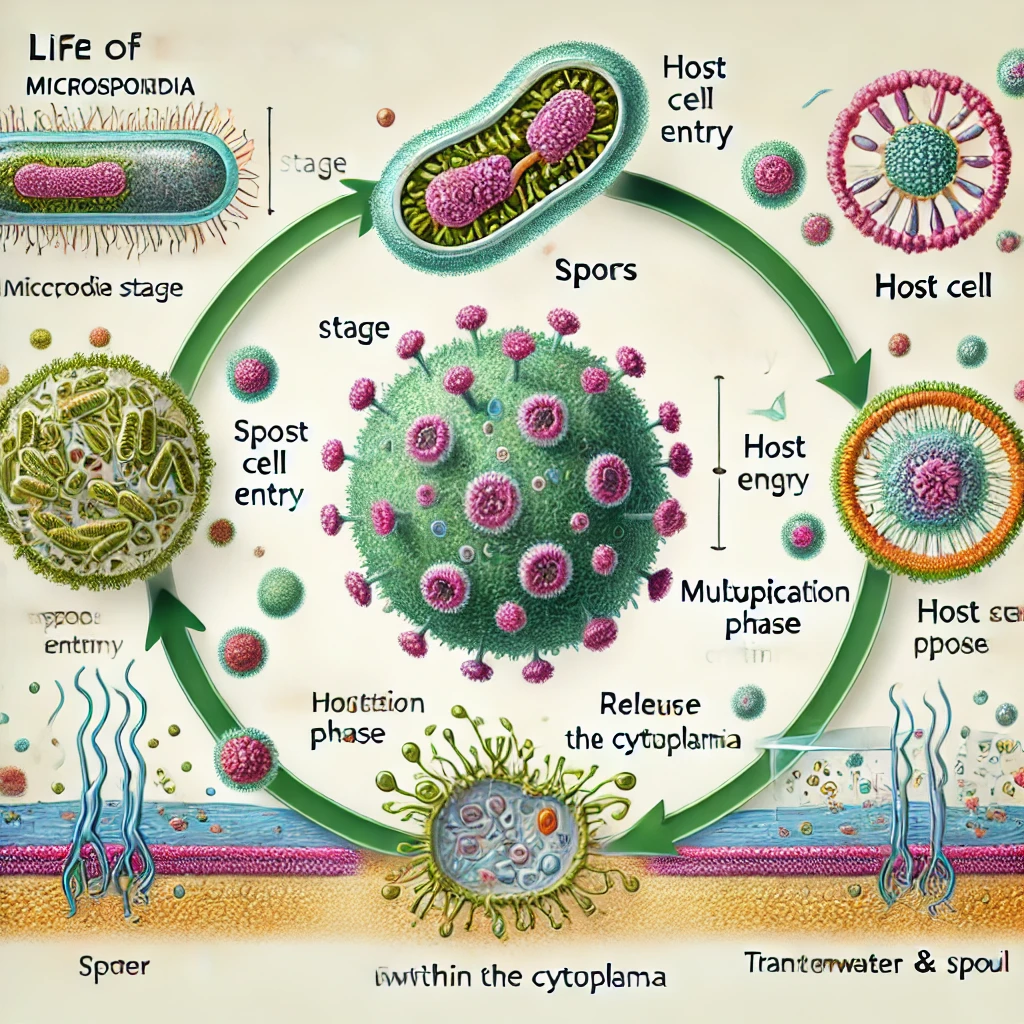
The Lifecycle of Microsporidia
Microsporidia’s lifecycle consists of distinct phases:
- Spore Stage: Dormant and highly resistant.
- Infection: Entry into host cells.
- Replication: Occurs within the host cytoplasm.
- Release: New spores exit the host to infect others.
Microsporidia’s Impact on Ecosystems
Microsporidia play complex roles in ecosystems:
- Regulation of Insect Populations: They infect and control pests like mosquitoes.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Affect fish health and biodiversity.
Microsporidia Pictures to Draw
Illustrating microsporidia helps understand their structure and lifecycle. Their spore morphology is easy to trace and provides educational insights.
Common Names for Microsporidia
Microsporidia are also referred to by various names, such as:
- Parasite fungi
- Obligate intracellular parasites
- Microsporidiosis agents
Conclusion
Microsporidia’s adaptability and resilience make them a formidable parasite. Their ability to travel, survive harsh conditions, and infect diverse hosts emphasizes the need for awareness and prevention. By understanding their lifecycle, transmission, and impact, we can better protect both humans and ecosystems from their effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
how does microsporidia spread to people?
Microsporidia spread through contaminated water, food, and direct contact with infected hosts or their waste.
how deadly is microsporidia on a scale of 1-10?
For immunocompromised individuals, its severity can reach 8-10.
can microsporidiosis be prevented?
Yes, by ensuring safe water, practicing hygiene, and avoiding contact with contaminated sources.
where is microsporidia found?
Microsporidia are found in soil, water, air, and within animal hosts.
how does microsporidia like to travel?
It uses environmental mediums like water and soil and rides on hosts like insects and birds.
what is the portal of entry for microsporidia?
Microsporidia enter through the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and ocular pathways.